Seohan Group
Great Challenge & Innovation!
Performance and History

- Selected for the World Class+ Project support program Development of a four‑wheel independent‑drive electrification module for future mobility (Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy)

- Winner of the IR52 Jang Young‑Sil Award (High‑strength constant-velocity joint for electric vehicles with carbon‑reduction technology)
- Prime Minister’s Commendation for Industrial Technology Promotion (New Technology Commercialization category)

- Received NET (New Excellent Technology) certification (Cast Iron H/Disc)
- Certified as a Specialized Company in Materials, Parts, and Equipment

- Received the Technology 5-Star 5★ rating (HMC)
- Received the certification as a company specializing in materials & components

- Received the Technology 5-Star 5★ rating (HMC)
- Received the certification as a company with Excellent job invention compensation
- Developed Damper Fork

- Received the Technology 5-Star 5★ rating (HMC)

- Received the Technology 5-Star 5★ rating (HMC)
- Excellent Product Development Partner Award (HMC)
- IR52 Jang Youngsil Award (Hybrid Disc)

- Developed Aluminum Knuckle & Carrier

- Lightweight Hybrid Disc New Technology Certification (NET)

- Research institute moved (Dongtan)
- Korea’s first LSJ that minimizes lateral vibration developed

- CJ with excellent rotational balance developed domestically

- Established Seohan Engineering Research Institute (Jincheon)
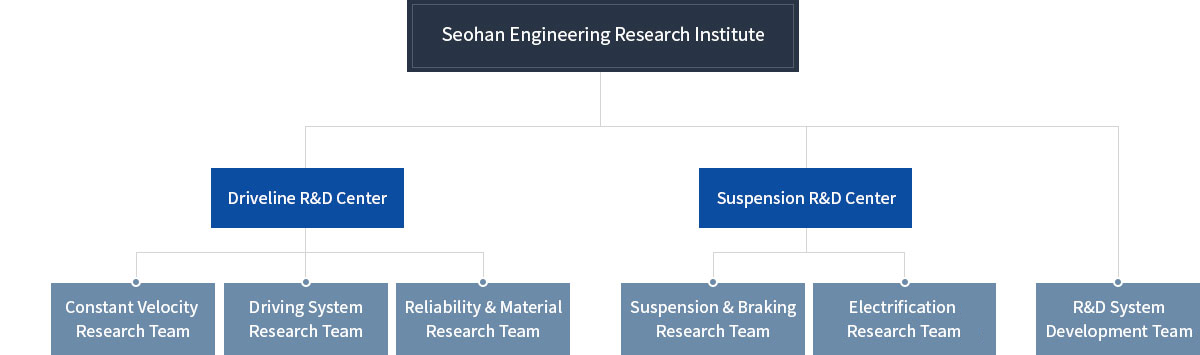
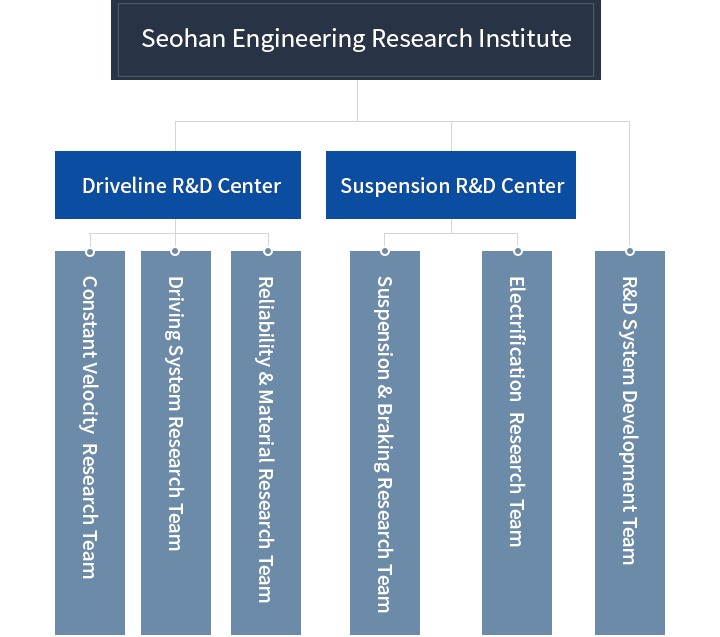
Corporate Organization
-
Research Facilities
 Office Building 3,147㎡ / Testing Center 3,150㎡ / Amenities 3,123㎡
Office Building 3,147㎡ / Testing Center 3,150㎡ / Amenities 3,123㎡ -
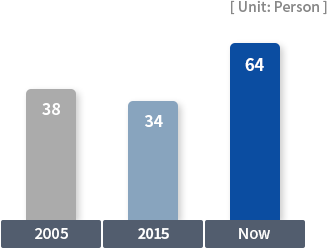
Researchers
-
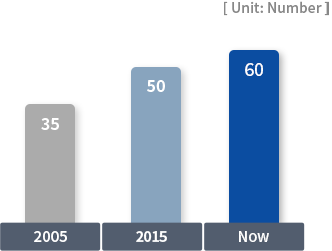
Research Equipment
Research & Development Areas
-
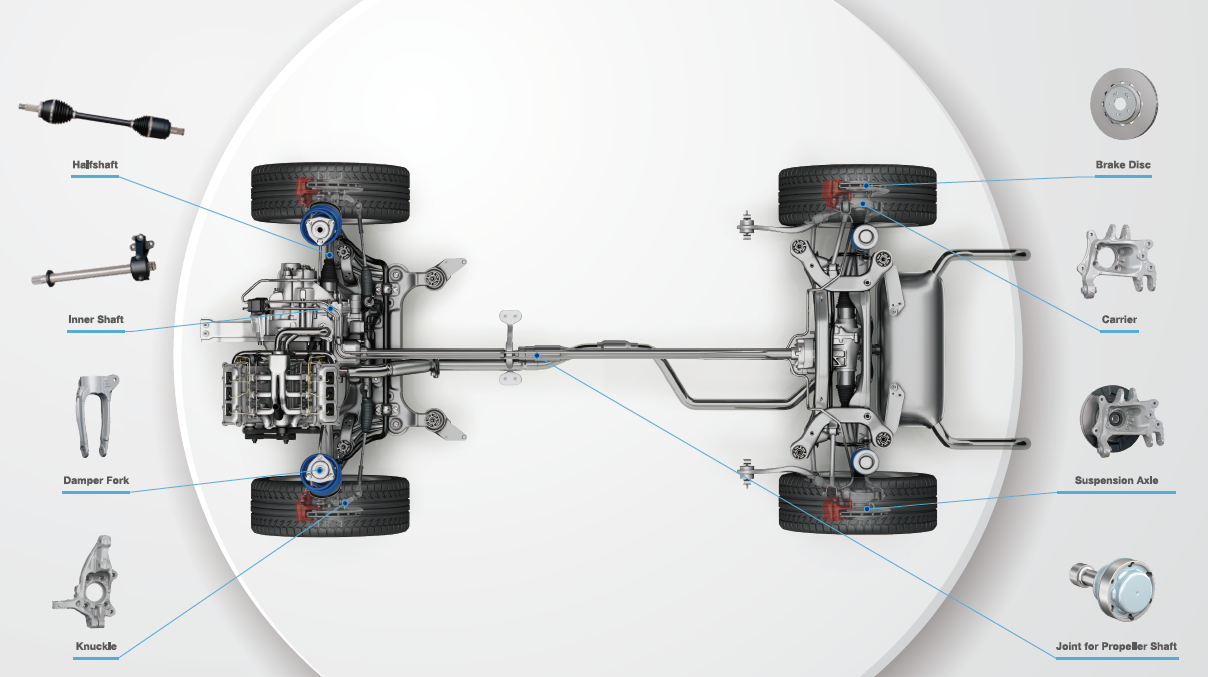
Fixed Joint
-
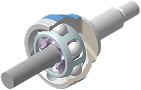
BJ
A standard wheel-side joint engineered for superior stability and durability by applying angular contact between the balls and the inner/outer track.
-

EUJ
A compact, 8-ball specification of the UBJ that enhances efficiency by reducing heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-

BJc
Engineered to be more compact and lightweight than the BJ specification, while securing identical strength and durability performance.
-

HBJ
This joint features a counter track to achieve a 52° maximum articulation angle, enhancing efficiency by lowering heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-

UBJ
This joint incorporates an undercut track to realize a maximum articulation angle of 50° and superior strength at high angles.
-

SJ
A dedicated rear-wheel joint incorporating a counter track, which boosts efficiency by reducing heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-
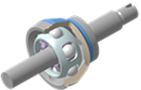
SUJ
Features a symmetrical undercut track to deliver a maximum articulation angle of 50° along with superior strength and durability at high angles.
-

FCJ
A dedicated rear-wheel joint featuring a cross-groove track that reduces heat generation, torque loss, and backlash.
-
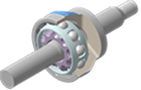
EBJ
A compact, 8-ball specification of the BJ that enhances efficiency by reducing heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-
-
Plunging Joint
-

TJ
A standard roller-type joint providing exceptional stability and durability.
-

TJC
Engineered to be more compact and lightweight than the TJ specification, while securing identical strength and durability performance.
-

LSJ
A roller kit type joint delivering superior low-vibration and NVH (GAF and PR) performance.
-

HLSJ
Features an improved articulation angle and sealing performance over the LSJ model.
-

DOJ
A ball-type joint equipped with a double offset straight track and a longer stroke than the TJ.
-
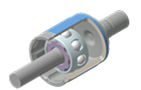
EDOJ
A compact, 8-ball specification of the DOJ that enhances efficiency by reducing heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-
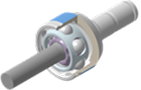
CJ
A joint incorporating a cross-groove track for superior NVH performance and minimized backlash.
-

ECJ
A compact, 8-ball specification of the CJ that enhances efficiency by reducing heat generation and minimizing torque loss.
-
-
Hollow Shaft
-

WTS (Friction Welding Tubular Shaft)
30% weight reduction compared to solid shaft, Improvement of NVH performance, High torsional stiffness
-

MTS (Monoblock Tubular Shaft)
40% weight reduction compared to solid shaft, Improvement of NVH performance, High torsional stiffness
-
-
Joints for Propeller shaft
-
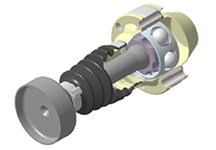
Disc CJ (Cross groove Joint)
- Maximum articulation angle: 4°
- Superior NVH performance
- Lightweight & compact design
-
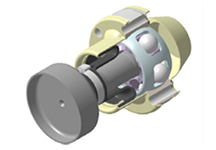
Disc BJ (Birfield Joint)
- Maximum articulation angle: 7°
- Suitable for high-speed rotation and high-angle vehicle models
- Compact design applying a J-shaped boot
-
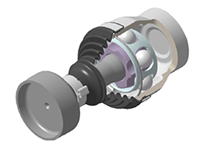
Monoblock CJ (Cross groove Joint)
- Maximum articulation angle: 4°
- Superior NVH performance
- Cost-effective and weight-reduced specification
-
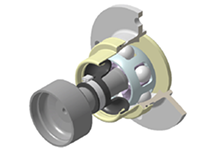
Flange BJ (Birfield Joint)
- 4-hole flange specification
- Suitable for high-speed rotation and high-angle vehicle models
- Compact design applying a J-shaped boot
-
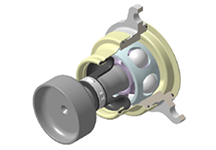
Flange CJ (Cross groove Joint)
- 3-hole flange specification
- Optimized for vehicle assembly process
- Lightweight design compared to the disc specification
-
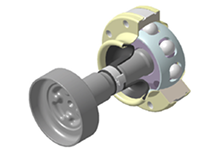
Disc HBJ (High efficiency Birfield Joint)
- 8-ball compact design
- High-torque and high-efficiency specification
- Superior durability from low heat generation
-
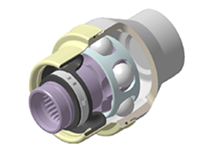
DCJ (Direct Connecting Joint)
- 8-ball monoblock design
- Excellent backlash performance
- Spline structure for direct assembly to the vehicle
-
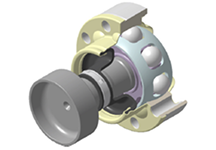
Disc PSJ (P/Shaft Symmetric offset Joint)
- 8-ball compact design
- Features a symmetrical track structure
- Superior durability from low heat generation
-
-
New Joints for Halfshaft
-
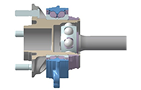


IDA (Integrated Drive)
A next-generation hub bearing that integrates the Hub and Halfshaft. Lightweight with high lateral rigidity. IDA Composition: Can be assembled by combining IDA with various joints like ECJ, FCJ, and EDOJ.
-
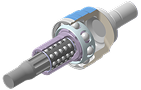
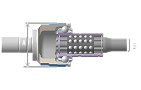
BSJ (Ball Spline Joint)
Integrates a ball spline design into the inner race of the lightweight, 8-ball SJ / FCJ joint. Maximum articulation angle of 32° and a plunging length of 62mm.
-
-
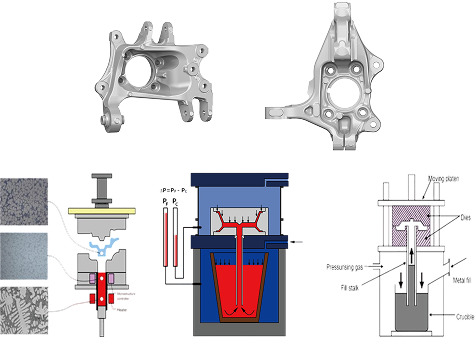
Aluminum Knuckle & Carrier
Casting methods (high pressure, counter pressure, low pressure)
Securing product competitiveness through diversification of manufacturing processes
-
Disc Machining & Surface Treatment
New machining process for braking surfaces
New surface treatment process

-
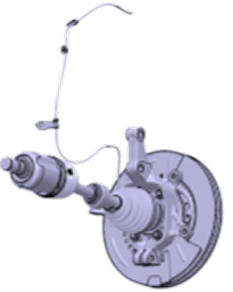
Modularization
Axle & Halfshaft, Axle & Brake Complete, Integrated Axle
Improved system performance
New system structure
-
All-Aluminum Disc Development
Achieves 50% weight reduction through all-aluminum construction, adapting to the future vehicle environment.

-
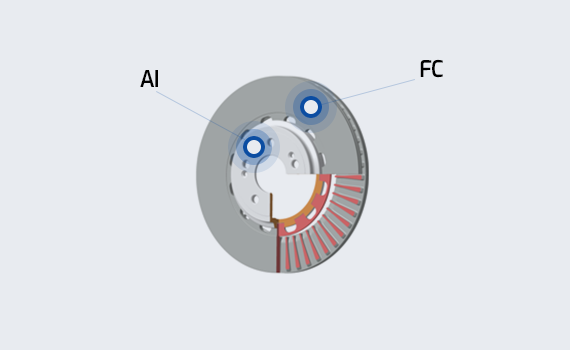
Aluminum Hybrid Disc Development
Realizes improved fuel efficiency and ride comfort by applying aluminum to the mounting area for weight reduction.
-
Cast Iron Hybrid Disc Development
Responds to the demands of EV platforms by improving strength and reducing weight through material changes.

-
Nitrided Disc Development for Rust Prevention
Achieves improved disc lifespan and functional enhancements through the development of a surface-nitrided disc.

Achievements of Research
-
 94Patents registered in Korea
94Patents registered in Korea -
 10Patents registered internationally
10Patents registered internationally -
 37Domestic and international applications
37Domestic and international applications -
 4Designs
4Designs